Cloud-Native HSM based on Intel Software Guard(SGX)
Patent
Cloud-Native HSM is a cloud-native Hardware Security Module(HSM) service that allows you to host encryption keys in the Intel Software Guard extension enclave and perform cryptographic operations accelerated by QAT in a cluster of HSM. You can manage the HSM resource with the Kubernetes customer resources, so you do not need to worry about scaling, managing, and clustering. You can leverage the Kubernetes’ function to provide the HSM to your service.
This is the architecture of the Cloud Native HSM.

- If the application needs an HSM device to create a secure connection with a remote host, you can deploy an HSM agent as a sidecar to work with the application Pod.
- And then, the application can call the HSM controller to generate a Key Pair and a CSR.
- The HSM controller received the request and then call the corresponding HSM manager to really create a Key Pair and Generate a CSR from the CTK for Intel SGX.
- After that, the application can take the CSR to the remote CA center to get a certificate.
- The application can put the received certificate to the SGX enclave and cross the HSM controller through the HSM manager.
- After getting the certificate, the Application can call the Crypoki through the PKCS#11 client and PKCS#11 server to the CTK.
Advantage:
- HSM agent works as a sidecar, and it won’t need to make any change in the application code. The application can use the Unix socket to involve the HSM. It keeps the safety of the HSM.
- HSM controller leverages the Kubernetes function to manage the HSM cluster, it’s convenient
- The SGX enhances the security of the data and private key.
If they use the CTK for Intel SGX as a sidecar, and use the Unix socket to forward the PKCS#11 service between the Pod they will hit the patent.
AWS Cloud HSM
What is Cloud Hardware Security Module(HSM)?
A hardware security module(HSM) is a computing device that processes cryptographic operations and provides secure storage for cryptographic keys.
AWS Cloud HSM is a cloud-based hardware security module (HSM) that enables you to genereate and use you own encryption keys.
Cloud HSM is a compliant with FIPS 140-2 level 3 (The Federal Information Processing Stanard Publication 140-2)
It automates administrative tasks like hardware provisioning, sofeware pathcing, high-availability, and backups
Applications can integrate with Cloud HSM using PKCS#11, Java Cryptography Extensions(JCE), and Microsoft CryptoNG (CNG) API libraries.
CloudHSM can scale quickly on-demand with no up-front costs.
Cloud HSM Cluster
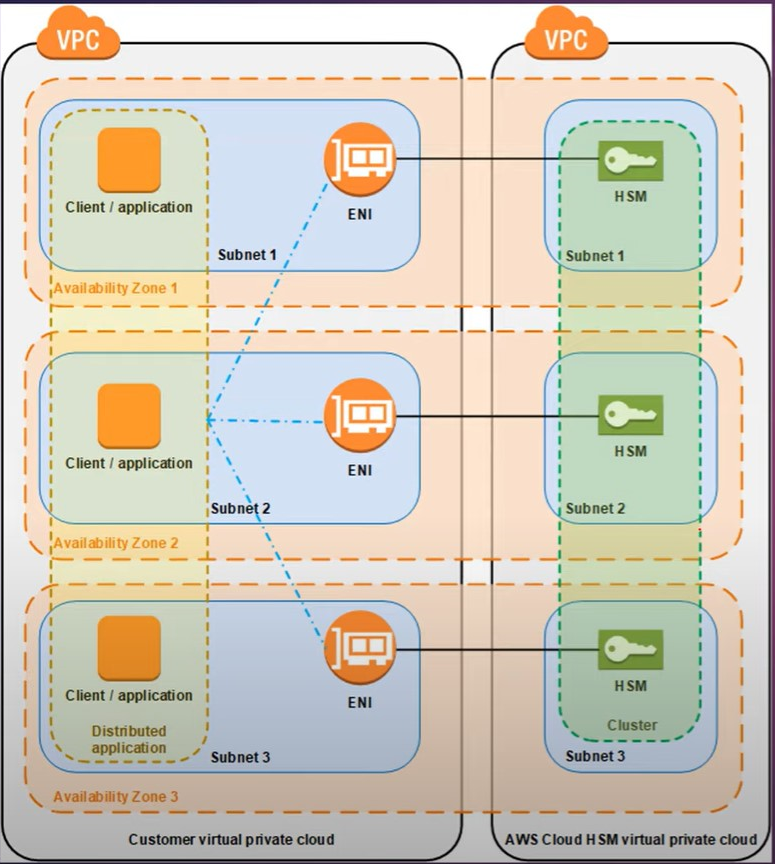
AWS Cloud HSM provides hardware securtiy modules (HSM) in a cluster.
A cluster is one logical HSM.
To interact with the HSMs in a cluster, you need the AWS Cloud HSM Client software.
Client can be installed on Amazon EC2 instances, known as client instances, that reside in the same VPC as the HSM ENIs.
When you perform a task or operation on the one HSM in a cluster, the other HSM in that cluster are automatically updated.
You can create a cluster that has from 1 to 28 HSMs (the defaut limit is 6 HSMs per AWS account per AWS region.)
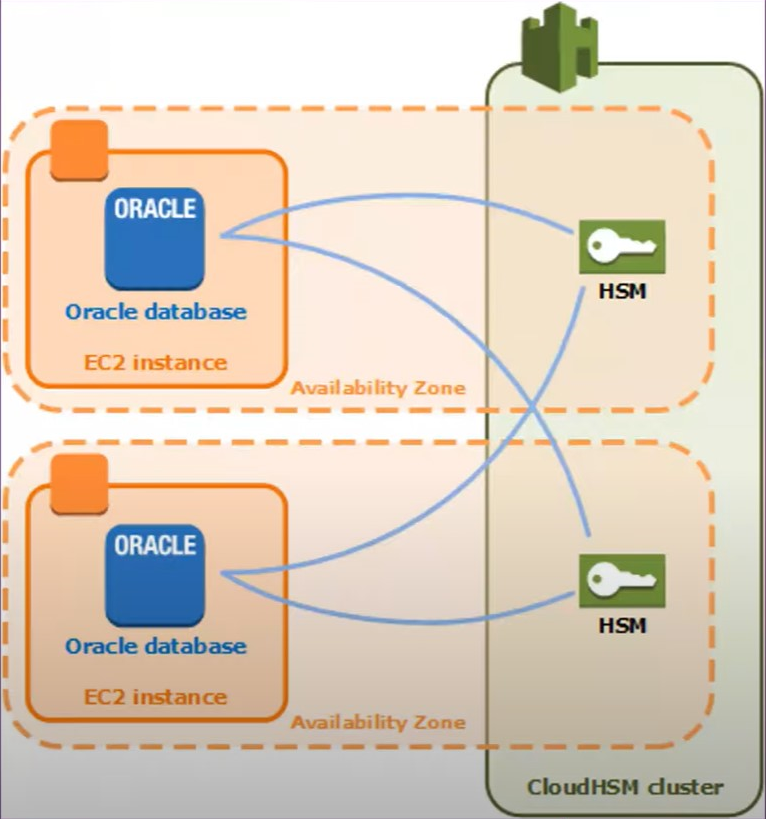
Benefits
- Generate and manager cryptographic keys
- Cluster based makes it easy to load balance and scale
- API based integration for Applications
- Integrates with AWS KMS to create custom key stores
Google Cloud HSM
Cloud HSM
Cavium Liquid Security HSM
Why Cloud HSM
Complicance
- FIPS 140-2 level 3 certified HSMs
Regionalization
- HSM keys are cryptographically bound to region
- Avaiable in all GCP Regions
- Support for multi-regions
No application changes for Cloud KMS customers
- Same API and client libraries as Cloud KMS
It leverages the exact same API as Cloud KMS, what that mean is that if you know how to use cloud KMS, then you know howe to use Cloud HSM.
Key Fearures:
- Global and multi-region support
- Attestation statement
- confidence your keys are hardware protected
- Cryptographically signed statement provided by the HSM verifying the creation of the key si within an HSM boundary and non-exportable
- statement can be verified manually or through a script
- verify key attriburtes
- CMEK integration
The HSM is bind with Vm not bind with application Pod
Tenant Separation
Summary
- Cloud HSM provides a scalable, reliable, and low-maintenance service
- Provides a modern, intergrated approach to administrative control and tenant isolation
- Keys can be effortlessly created in multi-regions or event a global region.
- HSM keys can be used to seamlessly protect your data-at-rest with CMEK services
- Look for an upcomming Cloud HSM white paper
What is a Cloud Hardware Security Module
The CloudHSM helps you meet corporate, contractual and regulatory compliance requirements for data security by using dedicated Hardware Secutiry Module(HSM) applicances withing the cloud.
very critical area in the cryptography, Stand out on CV, fundamental topic to learn for cloud security role.
1. Title of the invention
Cloud Native HSM based on Intel Software Guard Extension (SGX) And QAT
2. names of the inventors
Ren, Qiang 11717682
Ying, Ruoyu
Huang, Jiahao
3. TECHNOLOGY BACKGROUND
3.1 Problem Definition - What technical problem did you solve?
There are many scenarios that need Hardware security module (HSM) to protect transactions, identities, and applications. HSM is excel at storing cryptographic keys and provisioning encryption, decryption, authentication, and digital signing service for a wide range of applications. The dilemma here is that most cloud native services are hard to co-work with the traditional HSM that are physical devices. In the cloud native scenario, most applications need the capability of scaling and dynamic migration, but the physical HSM is hard to meet the requirement.
Cloud-Native HSM is a cloud-native Hardware Security Module service that allows you to host encryption keys or data in the Intel Software Guard extensions (SGX) enclave and perform cryptographic operations accelerated by Quick Assistant Technology (QAT) in a cluster of HSM. You can manage the HSM resource with the Kubernetes customer resources, so you do not need to worry about scaling, managing, and clustering. You can leverage the IA (Intel Architecture) features which are SGX to keep the private data security and QAT to accelerate the data encryption.
3.2 Previous Solutions (if any):
Currently, there are two main types of cloud HSM. One is to provide users with the right to use HSM as a single tenant on the physical level, such as Microsoft Azure Dedicated HSM. The cloud providers deploy HSM in different data centers. When the customer needs it, the cloud providers preconfigure HSM and connect it to the customer’s virtual network as a cloud HSM so that only the customer can access it. After the customer accesses the cloud HSM for the first time and changes the password, the cloud providers will no longer have the management rights of this cloud HSM. The customer can have full control and management rights.
This is a highly specialized service. This service is very secure and easy to migrate programs that directly access physical HSM. The service can meet the unique needs of some large organizations. However, due to excessive cost, complex configuration, inconvenient scaling, and resource waste, it is not suitable for many customers.
The second is to provide virtual HSM for users, such as AWS Cloud HSM. The cloud providers generate multiple virtual HSM on the physical HSM through virtualization technology, and users can obtain the access permission of the virtual HSM as a single tenant. Users can easily start and stop virtual HSM, build Cloud HSM clusters, and automatically synchronize virtual HSM by using relevant Cloud HSM API in their own virtual network. The users configure the corresponding client on their own virtual machine instances, and then applications on the virtual machine instances can use the virtual HSM cluster through a secure network connection between client and server.
This is the current mainstream service. Customers can quickly build virtual HSM clusters through the various APIs provided by cloud providers. In addition to this, customers can quickly scale clusters on demand. However, this service will also bring a lot of costs, which is often unacceptable for those who want to use the cloud to reduce costs. Secondly, the solution provides services to virtual machine instances through a virtual HSM cluster, which does not conform to the idea of cloud native. Managing virtual HSM clusters and secure Internet connections requires the use of dedicated resources and integration, so the operation capability has also proved to be a problem.
Figure 1: Architecture of AWS Cloud HSM
4. OVERVIEW OF THE INVENTION
4.1 Short summary – In 1-3 sentences, describe the core of your solution.
a. Cloud-Native HSM provides HSM service for applications only with SGX feature of CPU, and the QAT is optional for acceleration, do not need to plug in another physical device to the machine.
b. HSM agents work as a sidecar to provide Cryptoki for users’ application, which work as a usual physical device without code change for the application.
c. The private key and sensitive data stored in the SGX enclave, it’s safety.
d. The cryptographic operations can leverage the QAT to accelerate the process.
e. Cloud-Native HSM is a Kubernetes native service which has capability of scaling, migrating and reliability.
4.2 Advantages – In 1-3 sentences, describe the value of the invention to Intel or to our customers.
In general, the Cloud Native HSM agent provides HSM service based on the Intel Software Guard Extensions (SGX) that keep the private key in the enclave and only the applications pod can access it which keeps the sensitive data’s security. And the HSM agent can scale and migrate with the application pod, which is convenient. What’s more, Cloud Native HSM can leverage the QAT to accelerate the cryptographic operations.
Compared with the Cloud HSM, there is a risk for the transport between the application and the Cloud HSM. But, when using the Cloud HSM, the data will not leave the application Pod.
Cloud native HSM is especially suitable for the pod whose life cycle is consistent with that of confidential information, such as protecting the private key for a mutual SSL connection between to pod in service mesh from administrator attacks.
Cloud native HSM can also be used in combination with other security devices. For example, we can copy an existing private key from a Cloud HSM to the Cloud Native HSM, but not suggested.
For customers, the Cloud Native HSM provides them with a flexibility HSM device which can be managed by Kubernetes customer resources. It makes it much more convenient to use HSM in the cloud native application and much more secure for their application. The application can involve the Cloud Native HSM without code change.
For Intel, it is a good chance to promote the SGX technology to provide security service for most cloud native applications and promote the QAT technology to accelerate the encryption and decryption process. Thus, it is also helpful to promote our Sapphire Rapids Platform.
5. Detectability
5.1 Please describe in detail how your invention is detectable in a final product.
A. If your invention results in a specific structural feature please describe the appearance of that feature (e.g., include SEM/TEMs of actual features if available).
B. If there are visual inspection and/or reverse engineering techniques that can be used to identify the feature, please describe them.
If they use CTK for SGX work as a sidecar pod and forward the HSM token to the application pod through the Unix socket.
C. If documentation such as product literature would show usage of the invention, please let us know what to look for in that regard.
The cloud native application that wants to use HSM to provide a dedicated, secure, tamper-resistant environment to protect cryptographic keys and data, and to automate the lifecycle of those same keys. For example, the mutual SSL connection between to pod in service mesh like Istio.
6. DETAILS OF THE INVENTION
6.1 Provide details that help us fully understand your invention, including details on how you solved the technical problem, and at least one figure. You may also provide flowcharts, graphs, slides, or data to support your description. Where appropriate, please provide and explain any empirical support, such as experimental data or) simulation results, that can demonstrate the viability of your invention.
SoftHSM with Intel SGX/QAT: This works as a software HSM to provide enhancing the security of data and key protection applications by exposing interfaces. That runs the key generation and cryptographic operations securely inside an Intel Software Guard Extensions (SGX) enclave. And this can leverage the QAT to accelerate the cryptographic operations.
HSM Agent: HSM Agent is an operator of the HSM customer resource which aims at managing the local SoftHSM, to create tokens, create key pairs, generate CSR, add certificate to the SGX enclave, and even add an existing private key to the SoftHSM.
HSM Controller: The HSM Controller monitors the changing of the customer resource of HSM and calls the HSM Agent to apply the change of the resources.
PKCS#11 Client/Server: PKCS#11 Server is used to forward the HSM token in the HSM agent container to the application pod through Unix socket. PKCS#11 Client connects to the PKCS#11 Server by the Unix socket and provides Cryptoki API for the application. For the application, the PKCS#11 Client and server is transparent. The application calls the HSM token through the PKCS#11 API like locally.
Figure 2: Architecture of Cloud Native HSM
Figure 1 is the architecture of the Cloud Native HSM.
The default workflow is as follows.
\1. If the application needs an HSM device to create a secure connection with a remote host, you can deploy an HSM agent as a sidecar reside the application Pod.
\2. And then, the application can call the Kubernetes API to create a customer resource of HSM Key Pair as follows.
1apiVersion: soft-hsm-sgx.intel.com/v1alpha1
2kind: SoftHSMKeyPair
3metadata:
4 name: keypair-1
5 namespace: default
6spec:
7 name: keypair-1
8 applicationPod: application-1
9 token:
10 lable: "token-1"
11 slot: 0
12 soPin: 12345678
13 pin: 12345678
14 cert:
15 keyPair:
16 keyType: "rsa:2048"
17 lable: "keypair-1"
18 id: "0001"
19 subject: "/CN=application-1"
20
21
22apiVersion: soft-hsm-sgx.intel.com/v1alpha1
23kind: SoftHSMKeyPair
24metadata:
25 name: keypair-1
26 namespace: default
27spec:
28 name: keypair-1
29 applicationPod: application-1
30 token:
31 lable: "token-1"
32 slot: 0
33 soPin: 12345678
34 pin: 12345678
35 cert:
36 keyPair:
37 keyType: "rsa:2048"
38 lable: "keypair-1"
39 id: "0001"
40subject: "/CN=application-1"
41csr: CZ01fouDJIXLehgw62ol7TsuKC1CvUkVUiI=
apiVersion: soft-hsm-sgx.intel.com/v1alpha1 kind: SoftHSMKeyPair metadata: name: keypair-1 namespace: default spec: name: keypair-1 applicationPod: application-1 token: lable: “token-1” slot: 0 soPin: 12345678 pin: 12345678 cert: keyPair: keyType: “rsa:2048” lable: “keypair-1” id: “0001” subject: “/CN=application-1”
\3. After creating the customer resource, the HSM controller will call the specific HSM agent according the applicationPod field to generate a Key Pair in the SGX enclave, and a CSR is created write back the SoftHSMKeyPair for the certificate request, which is a base64 encode string.
apiVersion: soft-hsm-sgx.intel.com/v1alpha1 kind: SoftHSMKeyPair metadata: name: keypair-1 namespace: default spec: name: keypair-1 applicationPod: application-1 token: lable: “token-1” slot: 0 soPin: 12345678 pin: 12345678 cert: keyPair: keyType: “rsa:2048” lable: “keypair-1” id: “0001” subject: “/CN=application-1” csr: CZ01fouDJIXLehgw62ol7TsuKC1CvUkVUiI=
\4. When the application pod found the CSR field is not empty, the applications can call the remote CA center to get a certificate for themselves.
\5. The application can put the received certificate to the pem filed with base64 encode in the customer resource of SoftHSMKeyPair. And then, the HSM controller will write the cert to the SoftHSM in SGX enclave cross the HSM controller and the HSM manager.
apiVersion: soft-hsm-sgx.intel.com/v1alpha1 kind: SoftHSMKeyPair metadata: name: keypair-1 namespace: default spec: name: keypair-1 applicationPod: application-1 token: lable: “token-1” slot: 0 soPin: 12345678 pin: 12345678 cert: keyPair: keyType: “rsa:2048” lable: “keypair-1” id: “0001” subject: “/CN=application-1” csr: CZ01fouDJIXLehgw62ol7TsuKC1CvUkVUiI= pem: y9EelphCnI2MFUvbVZ3YUl3aHhwcHRaY2g2OFQ2TGJyQml2dk9xSFA
\6. Finally, the application can call the Cryptoki through the PKCS#11 client and PKCS#11 server to the SoftHSM. The PKCS#11 client and PKCS#11 server are connected by the Unix socket mounted in a shared point. The application can offload the cryptographic operations to the HSM Agent container which use SGX for keep the security and QAT for acceleration.
If you already have an existing keypair and cert, you can use the Cloud Native HSM as follows.
\1. If the application needs an HSM device to create a secure connection with a remote host, you can deploy an HSM agent as a sidecar reside the application Pod.
\2. The application can call the Kubernetes api to create a customer resource SoftHSMKeyPair with existing keypair and cert which are base64 encoded like as follows:
apiVersion: soft-hsm-sgx.intel.com/v1alpha1 kind: SoftHSMKeyPair metadata: name: keypair-1 namespace: default spec: name: keypair-1 applicationPod: application-1 token: lable: “token-1” slot: 0 soPin: 12345678 pin: 12345678 privateKey: VZ3YUl3aHhwcHRaY2g2OFQ2 publicKey: 7TsuKC1CvUkVUi cert: keyPair: keyType: “rsa:2048” lable: “keypair-1” id: “0001” subject: “/CN=application-1” csr: CZ01fouDJIXLehgw62ol7TsuKC1CvUkVUiI= pem: y9EelphCnI2MFUvbVZ3YUl3aHhwcHRaY2g2OFQ2TGJyQml2dk9xSFA
\3. After creating the customer resource, the HSM controller will call the specific HSM agent according the applicationPod field to create a Key Pair with the existing key, and save the certificate in the SGX enclave.
\4. Finally, the application can call the Cryptoki through the PKCS#11 client and PKCS#11 server to the SoftHSM. The PKCS#11 client and PKCS#11 server are connected by the Unix socket mounted in a shared point. The application can offload the cryptographic operations to the HSM Agent container which use SGX for keep the security and QAT for acceleration.
TODO:
- Add load balance to this architecture
- QAT accelerate
- Attestation
- Dedicated Device is expensive
